- Home
- Symptoms Directory
- Low testosterone symptoms
Low testosterone symptoms: What are the early signs of low T?

Overview: What does low testosterone feel like?
Low testosterone—also called testosterone deficiency syndrome (TDS), hypogonadism, or just “low T”—occurs when the testicles don’t make enough of the male sex hormone testosterone.
It’s usually experienced as a lowered interest in sex, a decrease in spontaneous erections, fatigue, and low energy. In addition, men with low testosterone may put on weight, lose muscle mass, and feel less physically strong. Mood and concentration can also suffer.
Women can also have low testosterone, although their normal testosterone levels are only a fraction of men’s. For women, the experience of low testosterone includes lowered libido, weakness, tiredness, mood changes, and weight gain.
Is low testosterone something to worry about? It does affect quality of life and, left untreated, can sometimes lead to more severe problems.
Key takeaways:
Low testosterone is a common health condition that mostly affects older men but can affect anyone regardless of age, sex, race, or ethnicity.
Early signs of low testosterone include a decreased interest in sex, a reduction in spontaneous erections, and a decrease in the volume of ejaculate.
Serious complications of low testosterone such as bone loss, anemia, or cardiovascular problems may require immediate medical attention.
Low testosterone is caused by aging, pituitary gland problems, obesity, diabetes, surgery, cancer treatment, tumors, hormone imbalances (such as high prolactin levels or low thyroid hormone levels), injury, HIV/AIDS, stress, or prescription drugs. You may be at risk for developing low testosterone symptoms if you have any of these conditions.
Low testosterone requires a medical diagnosis.
Symptoms of low testosterone generally do require treatment. They typically resolve with treatment within several months.
Treatment of low testosterone may include testosterone replacement therapy. Read more about low testosterone treatments here.
Untreated low testosterone could result in complications like bone loss, erectile dysfunction, and cardiovascular disease.
Save on prescriptions for low testosterone with a SingleCare prescription discount card. Use coupons for Androderm, Natesto, and testosterone to save up to 80%.
What are the most common signs of low testosterone?
In adults, the most suggestive signs of low testosterone are primarily sexual problems:
Decreased libido
Reduction in spontaneous erections
Decrease in ejaculate volume
Other common signs of low testosterone include:
Fatigue
Feeling tired
Diminished energy, vitality, and well-being
Sleeping problems
Mood changes
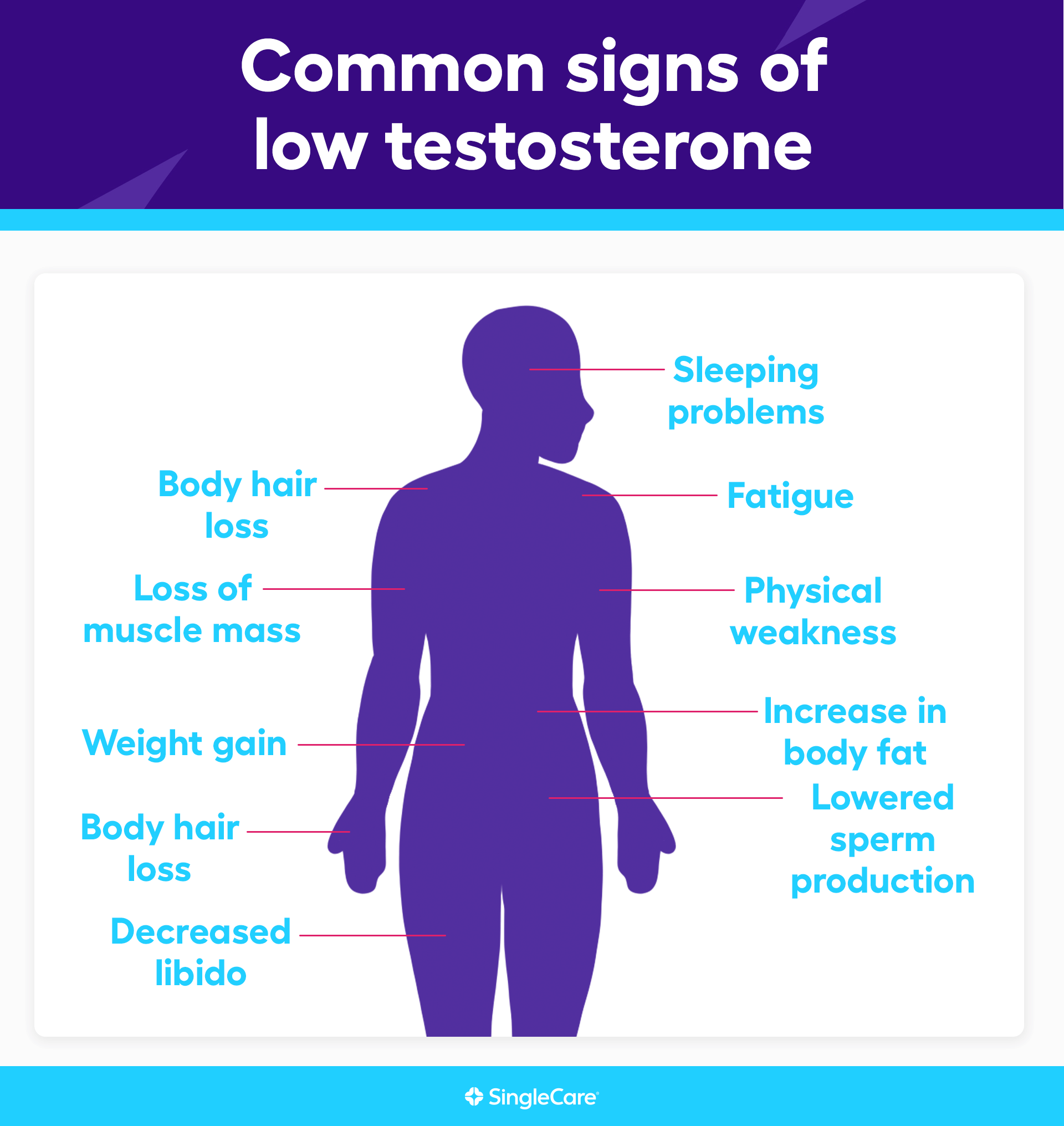
Other low testosterone symptoms
Other signs that suggest low levels of testosterone include:
Physical weakness
Loss of muscle mass
Weight gain
Increase in body fat
Body hair loss
Breast development (gynecomastia)
Lowered sperm production
Decreased testicle size
More serious low testosterone symptoms include:
Hot flashes and sweats
Difficulty concentrating
Infertility
Shrunken testicles
Bone loss (osteoporosis)
Anemia
If low testosterone causes bone loss, symptoms include:
Loss of height
Stooping
Broken bones
Lower back pain
If low testosterone reduces red blood cell counts, symptoms include:
Fatigue
Weakness
Shortness of breath
Cold feet and cold hands
Lightheadedness
Dizziness
Heartbeat irregularities
In children and teens, one of the most prominent signs of low testosterone is incomplete or delayed sexual development. Teens with low testosterone most often complain about tiredness and fatigue rather than sexual dysfunction.
Low testosterone symptoms in women
Low testosterone typically strikes women after menopause. The signs of low testosterone in women are not well-established but may include:
Low sex drive
Fatigue
Low energy levels
Weakness
Mood changes
Sleep problems
Weight gain
Difficulty concentrating
As with men, low testosterone can contribute to osteoporosis or raise the risk for cardiovascular problems in women.
Low testosterone symptoms in men
Men will typically notice low androgen levels because of erection and ejaculation issues, symptoms that women will not experience. For some men, sexual dysfunction may be motivation enough to seek the help of a healthcare professional.
Types of low testosterone: How can I tell which one I have?
Healthcare professionals distinguish between two different types of low testosterone: primary hypogonadism and secondary hypogonadism. In both types, the testicles do not produce enough testosterone.
In primary hypogonadism, the problem is with the testicles due to problems such as injury, genetics, undescended testicles, or cancer chemotherapy. Secondary hypogonadism is due to a problem with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, not the testicles. A number of causes are possible, but, in many cases, these other causes will have other symptoms. Some may already be diagnosed and undergoing treatment.
Distinguishing between primary and secondary hypogonadism is something only a physician can do after an examination and diagnostic tests.
RELATED: Medications that cause low libido
When to see a doctor for low testosterone symptoms
Both men and women should see a doctor if signs of low testosterone are experienced. There may be a more serious problem at work. Over time, low testosterone can be a risk factor for osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease in men and women. None of the symptoms of low testosterone, however, require emergency medical attention.
A doctor will usually perform a physical examination and take a medical history. Be prepared to answer questions about symptoms, health conditions, prescription drugs being used, and lifestyle. A morning blood test will be required to finalize the diagnosis. Other tests may be administered to find the cause of low testosterone.
Complications of low testosterone
Untreated low testosterone can be associated with bone density loss (osteoporosis), cardiovascular disease (including heart attack and stroke), cognitive impairment, mood problems, depression, and weight gain.
How to treat low testosterone symptoms
Low testosterone is treated with testosterone replacement or supplementation. Testosterone can be administered as an injection, applied as a transdermal patch, used as a topical gel or gum patch, inhaled as a nasal gel, taken orally as a pill, or implanted under the skin as a pellet. Oftentimes, the patch or topical gel is chosen. For women, there are no approved products or generally recommended doses of testosterone.
Not everyone will be a suitable candidate for testosterone replacement because of medical conditions such as prostate cancer, breast cancer, an abnormally high red blood cell concentration in the blood called polycythemia, severe and untreated obstructive sleep apnea, or other conditions. Men who are trying to get a partner pregnant should not be given testosterone because it significantly lowers sperm counts. Other men may need to be taken off testosterone therapy because of side effects.
If testosterone treatment is stopped, a urologist may prescribe an aromatase inhibitor (a breast cancer treatment), selective estrogen receptor modulator (another breast cancer treatment), or Pregnyl (human chorionic gonadotropin) instead. Only Pregnyl has been approved by the FDA for low testosterone. There are no guidelines for symptomatic treatment of low testosterone.
However, lifestyle changes have been shown to increase testosterone levels in men with hypogonadism. These include:
Losing weight
Exercising
Getting enough sleep by practicing good sleep hygiene
Eating a healthy diet
RELATED: Does working out increase testosterone?
Living with low testosterone
Lifestyle changes can help boost low testosterone levels. Excess weight contributes significantly to lowering testosterone, so losing weight has equivalent effects in increasing testosterone. A small study of 40 men on a ketogenic diet for at least 8 weeks showed a significant increase in total testosterone levels.
Getting enough sleep, exercising, and eating a healthy diet also help raise testosterone levels. Men with low testosterone should avoid smoking and, if they have a metabolic disorder, keep blood sugar or blood pressure under control.
Most importantly, see a healthcare provider
Low testosterone can have a significant effect on both quality of life and health. It can be successfully treated with hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle changes, or both. Over time, low testosterone can affect health and well-being by depleting bone density, depressing mood, sapping energy, and making it hard to concentrate and think. The good news is this: people don’t have to live with the symptoms of low testosterone or the risk.
While low LT is not an emergency, people experiencing low testosterone symptoms should talk to a healthcare professional. A doctor will be able to determine the exact cause of the symptoms and the most appropriate treatment options to manage the underlying condition.
RELATED: Does Medicare cover HRT?
FAQs about low testosterone symptoms
What causes low testosterone in young males?
Most of the problems that cause low testosterone production in older males can cause low testosterone in younger men. Except, of course, aging. Additionally, younger males are less likely to have high blood pressure or diabetes, but both are possible at any age.
RELATED: Top men’s health issues by age
What are the signs of low testosterone in a child?
A boy with low testosterone will not go through puberty, so delayed puberty is often the most obvious sign of low testosterone in a child. Growth rates can be affected, and their voice won’t deepen, their muscles won’t develop, and hair growth will be limited. Boys with hypogonadism may also show breast development or seem overly fatigued.
What are the signs of low testosterone by age?
The most obvious sign of hypogonadism in preadolescent boys is delayed puberty, but there may be other signs such as fatigue or difficulty concentrating.
Adolescents with low testosterone often do not have many of the same symptoms as adults. Erectile dysfunction and lowered sexual drive are usually not common complaints of teens with low testosterone. Instead, they have problems with fatigue and low energy. As with adults, a diagnosis can’t be made until a blood test is performed.
Young adults and older adults have many of the same symptoms. However, because older men may already have decreased testosterone and other aging issues, symptoms like enlarged breast tissue, muscle loss, low energy, weight gain, reduced physical performance, and even decreased sexual interest may already seem normal before testosterone levels become low enough to merit a diagnosis.
What’s next? Additional resources for people with low testosterone symptoms
Test and diagnostics
Diagnosing and managing low serum testosterone, Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings
Evaluation and management of testosterone deficiency: American Urological Association guideline, The Journal of Urology
Hypogonadism, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
Hypogonadism, StatPearls
Treatments
Low testosterone in adolescents & young adults, Frontiers in Endocrinology
Low testosterone treatment and medications, SingleCare
Testosterone therapy: review of clinical applications, American Family Physician
Treatment of men with central hypogonadism: alternatives for testosterone replacement therapy, International Journal of Molecular Science
What you need to know about low T, SingleCare
Scientific studies and clinical trials
Effectiveness of a very low calorie ketogenic diet on testicular function in overweight/obese men, Nutrients
Prevalence of hypogonadism in males aged at least 45 years: the HIM study, International Journal of Clinical Practice
More information on related health conditions
Erectile dysfunction treatment and medications, SingleCare
Hyperprolactinemia, Endocrine Society
Hypothyroidism treatment and medications, SingleCare
Klinefelter syndrome, National Institutes of Health
What are undescended testicles (cryptorchidism)?, Urology Care Foundation
Chad Shaffer, MD, earned his medical doctorate from Penn State University and completed a combined Internal Medicine and Pediatrics residency at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. He is board certified by the American Board of Internal Medicine and the American Board of Pediatrics. He has provided full-service primary care to all ages for over 15 years, building a practice from start up to over 3,000 patients. His passion is educating patients on their health and treatment, so they can make well-informed decisions.
...Related Drugs
Related Drug Information
Popular Prescriptions
Support
- Email Us Contact Us
- 24 Hours, 7 Days a Week
(Except Major Holidays)
- Customer Support 844-234-3057
- Provider Support 800-960-6918
Press Center
© 2024 SingleCare Administrators. All Rights Reserved.
* Prescription savings vary by prescription and by pharmacy, and may reach up to 80% off cash price.
Pharmacy names, logos, brands, and other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
This article is not medical advice. It is intended for general informational purposes and is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. If you think you may have a medical emergency, immediately call your physician or dial 911.
This is a prescription discount plan. This is NOT insurance nor a Medicare prescription drug plan. The range of prescription discounts provided under this discount plan will vary depending on the prescription and pharmacy where the prescription is purchased and can be up to 80% off the cash price. You are fully responsible for paying your prescriptions at the pharmacy at the time of service, but you will be entitled to receive a discount from the pharmacy in accordance with the specific pre-negotiated discounted rate schedule. Pharmacy names, logos, brands, and other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.Towers Administrators LLC (operating as 'SingleCare Administrators') is the authorized prescription discount plan organization with its administrative office located at 4510 Cox Road, Suite 111, Glen Allen, VA 23060. SingleCare Services LLC ('SingleCare') is the vendor of the prescription discount plan, including their website.website at www.singlecare.com. For additional information, including an up-to-date list of pharmacies, or assistance with any problems related to this prescription drug discount plan, please contact customer service toll free at 844-234-3057, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week (except major holidays). By using the SingleCare prescription discount card or app, you agree to the SingleCare Terms and Conditions found at https://www.singlecare.com/terms-and-conditions
© 2024 SingleCare Administrators. All Rights Reserved.